Premutation Fragile X Syndrome
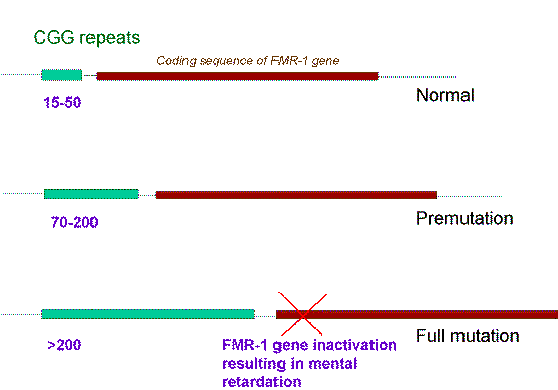
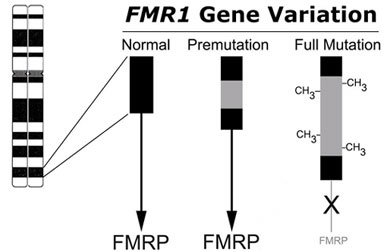
Premutation fragile x syndrome. Carriers of the fragile X premutation FPM have CGG trinucleotide repeat expansions of between 55 and 200 in the 5-UTR of FMR1 compared to a CGG repeat length of between 5. We identified 89 pregnant women with an expanded FMR1 gene seeking prenatal diagnosis. Fragile X Syndrome and Premutation Disorders.
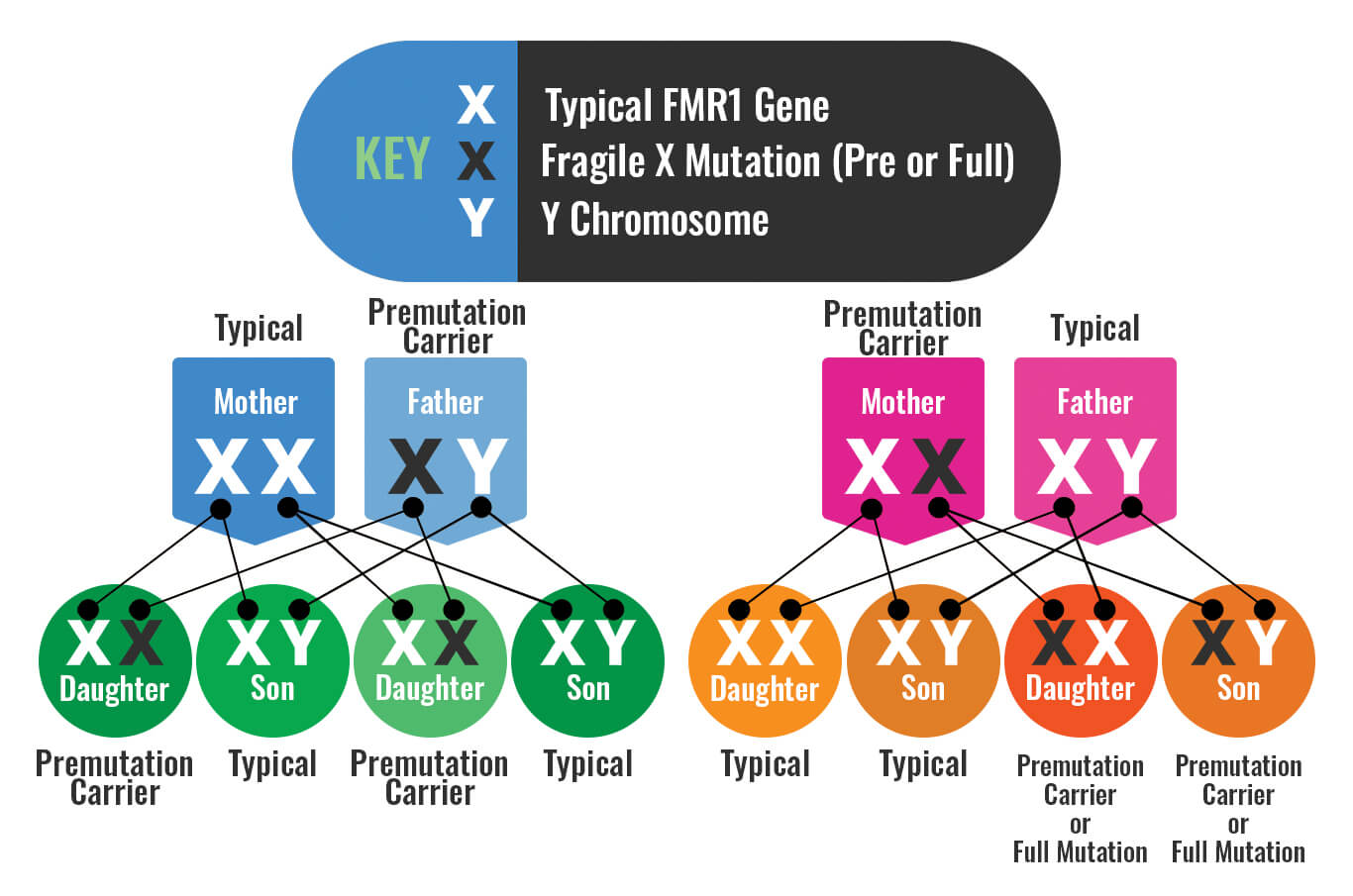
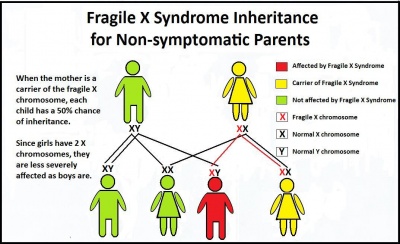
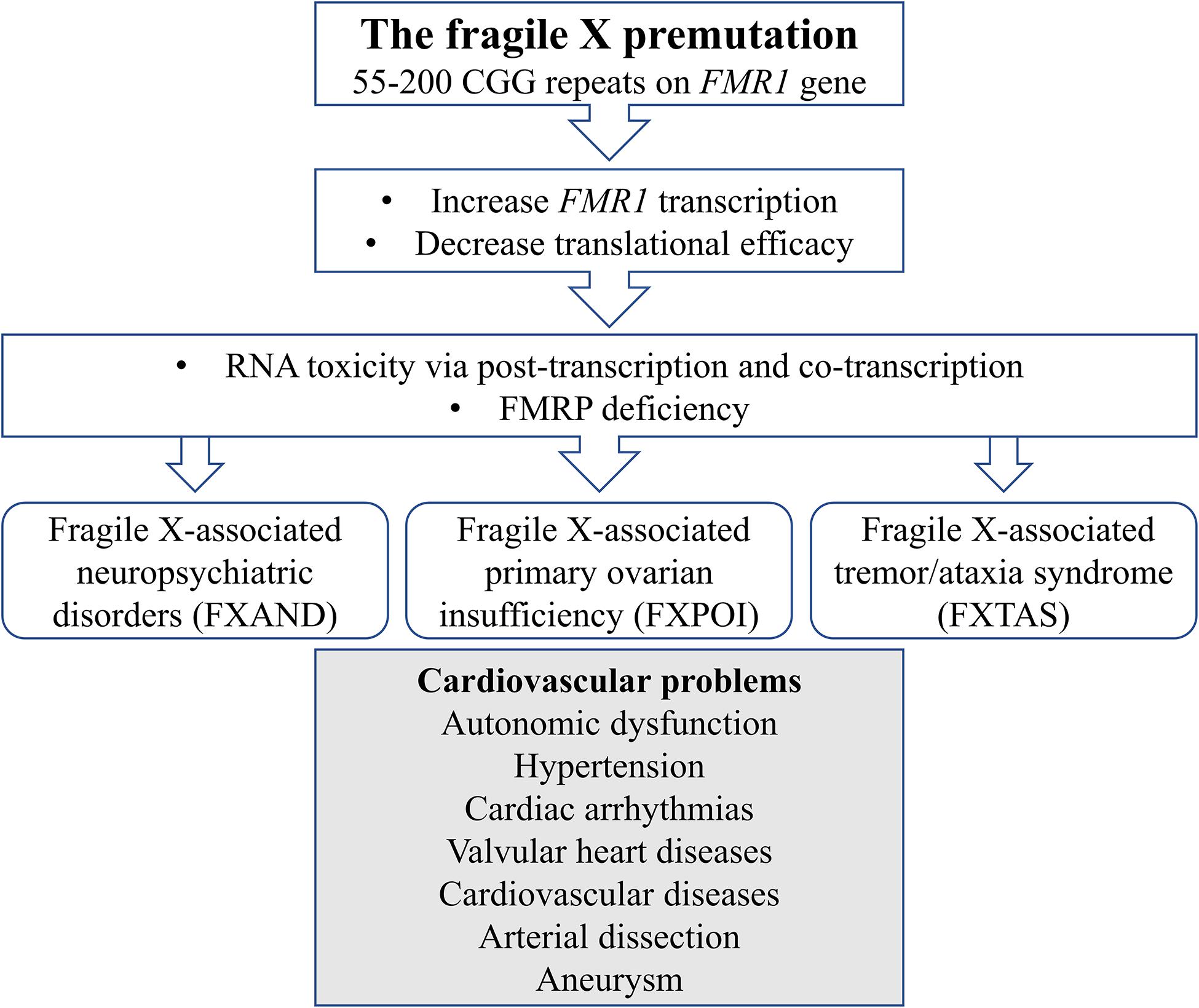
The fragile X-associated tremorataxia syndrome FXTAS is characterized by late-onset progressive cerebellar ataxia and intention tremor in males who have a premutation. There is increasing evidence that neurodevelopmental differences in people with Fragile X syndrome FraX may be explained by differences in glutamatergic metabolism. A male carrier will pass his premutation as a premutation not a full mutation on to all of his daughters and none of his sons.
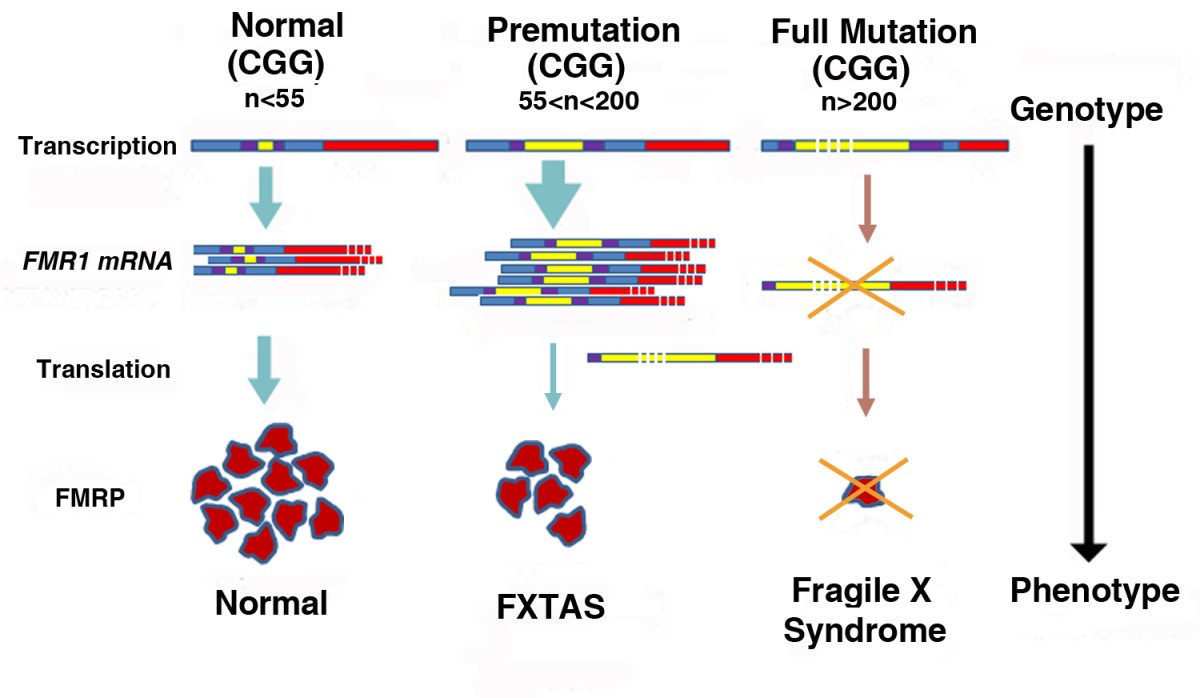
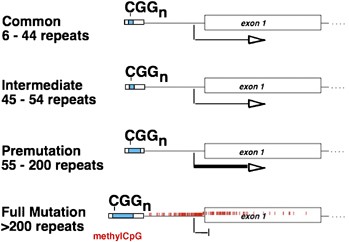
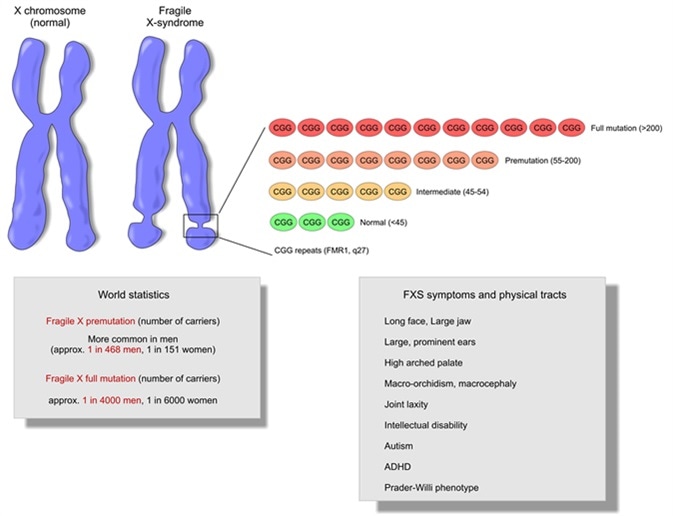
Fragile X premutation carriers have 55-200 CGG repeats in the 5 untranslated region of the FMR1 gene. Fragile X syndrome occurs in individuals with an FMR1 full mutation or other loss-of-function variant and is nearly always characterized in affected males by developmental delay and intellectual disability along with a variety of behavioral issues. The pattern of inheritance in the fragile X fraX mutation follows a multistage intergenerational process in which the premutation evolves into the full mutation and the characteristic phenotype of the fraX syndrome after passing through oogenesis or a postzygotic event.
Carriers may pass on an expanded mutation to a child or grandchild causing fragile X syndrome. Whereas full mutation CGG-repeat expansions 200 repeats of the fragile X gene FMR1 give rise to the neurodevelopmental disorder fragile X syndrome FXS. Smaller premutation expansions 55 to 200 repeats are now gaining increasing recognition as the basis for a spectrum of clinical involvement from neurodevelopmental problems.
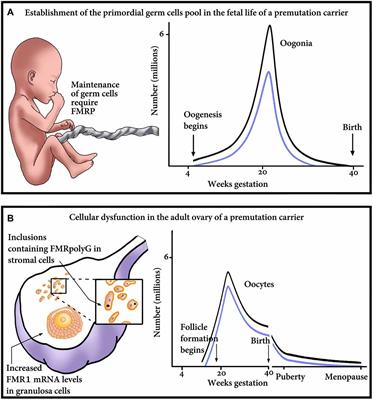
Amniocentesis or chorion villus sampling CVS was offered and a DNA test of the FMR1 gene was carried out in such pregnancies. Premutation carriers of FraX were originally considered to be unaffected although several recent reports demonstrate neuroanatomical cognitive and emotional differences from controls. To mid-adult disorders such as primary ovarian insufficiency and.
There is no reported risk for a male premutation carrier to have a daughter with Fragile X syndrome. The overall risk of full mutation among women N 21 with a repeat size between 60 and 80 was 48 one fetus with mosaicism and. Couples who carry the premutation or full mutation should be offered genetic and preconceptual counseling prior to attempting to conceive.
Males can also carry the Fragile X premutation. Males who have a premutation with 59 to 200 CGG trinucleotide repeats are usually unaffected and are at risk for fragile X-associated tremorataxia syndrome FXTAS.
Males can also carry the Fragile X premutation.
What is a premutation carrier. The Fragile X premutation may also present with a spectrum of disorders related to the fragile X gene FMR1. Whereas full mutation CGG-repeat expansions 200 repeats of the fragile X gene FMR1 give rise to the neurodevelopmental disorder fragile X syndrome FXS. To mid-adult disorders such as primary ovarian insufficiency and mood and psychiatric disorders. Fragile X is also a major cause of premature ovarian failure and irregular menses and it can subsequently affect fertility. Autism spectrum disorder is present in 50-70 of individuals with FXS. The pattern of inheritance in the fragile X fraX mutation follows a multistage intergenerational process in which the premutation evolves into the full mutation and the characteristic phenotype of the fraX syndrome after passing through oogenesis or a postzygotic event. There is increasing evidence that neurodevelopmental differences in people with Fragile X syndrome FraX may be explained by differences in glutamatergic metabolism. Some carriers also develop fragile X-associated disorders.
The overall risk of full mutation among women N 21 with a repeat size between 60 and 80 was 48 one fetus with mosaicism and. Amniocentesis or chorion villus sampling CVS was offered and a DNA test of the FMR1 gene was carried out in such pregnancies. Smaller premutation expansions 55 to 200 repeats are now gaining increasing recognition as the basis for a spectrum of clinical involvement from neurodevelopmental problems. Fragile X is also a major cause of premature ovarian failure and irregular menses and it can subsequently affect fertility. The fragile X-associated tremorataxia syndrome FXTAS is characterized by late-onset progressive cerebellar ataxia and intention tremor in males who have a premutation. Carriers may pass on an expanded mutation to a child or grandchild causing fragile X syndrome. The pattern of inheritance in the fragile X fraX mutation follows a multistage intergenerational process in which the premutation evolves into the full mutation and the characteristic phenotype of the fraX syndrome after passing through oogenesis or a postzygotic event.





























Post a Comment for "Premutation Fragile X Syndrome"