Horner's Syndrome In Horses
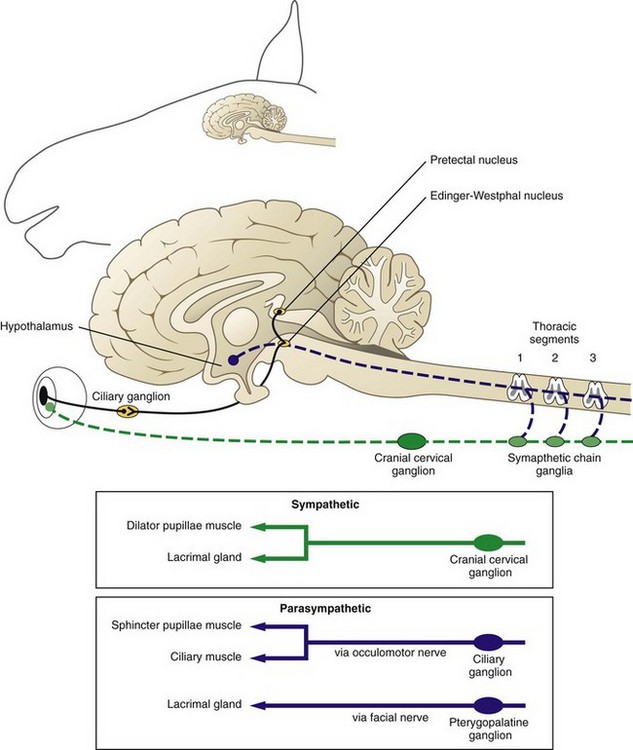
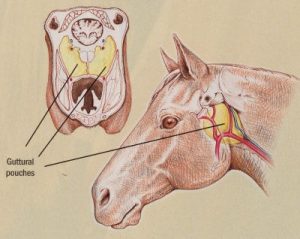
Horner's syndrome in horses. Horners syndrome is a mix of symptoms that are caused when theres a. The signs and symptoms occur on the same side ipsilateral as it is a lesion of the sympathetic trunk. Horners syndrome in large animals The sympathetic nervous innervation of the head was surgically transected in the horse cow sheep and goat.
Horners syndrome is a fairly common clinical manifestation that has been described in horses as well as other species as a cause of careless jugular venipuncture or perivascular injection Sweeney and Sweeney 1984 SWEENEY RW. The most prominent symptoms of equine Horners syndrome were ptosis local. Hahn Miscellaneous Disorders of the Equine Nervous System.
Search for more papers by this author. Techniques in Eq Practice Vol 5 Issue 1 Mar 2006 pp. None of the clinical signs in this series were transient.
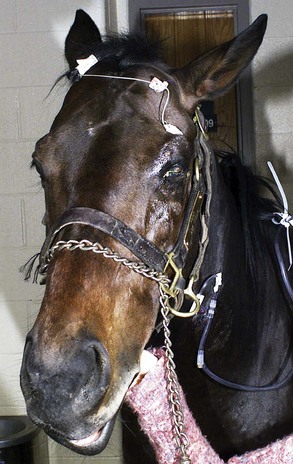
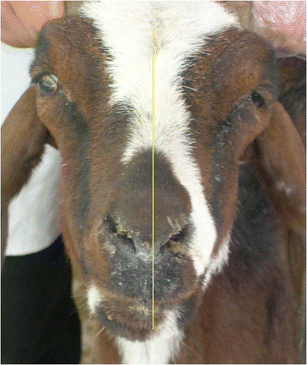
Horners syndrome is due to a dysfunction of the sympathetic nerves of the eyes and surrounding facial muscles. Note smaller angle of eyelashes on the left side. Experimental induction and a case report.
Horners Syndrome in 10 Horses Canadian Veterinary Journal Volume 33 May 1992. The Horners syndrome manifested as a result of the iatrogenic lesion varied. Horners Syndrome occurs when the parasympathetic nerve becomes dysfunctional.
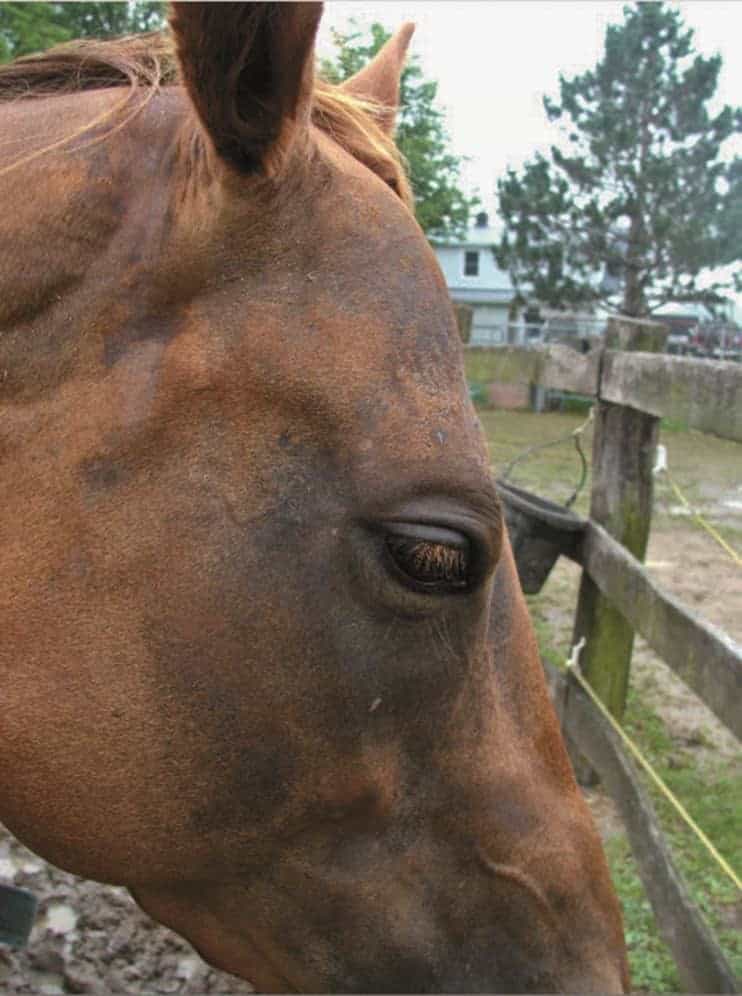
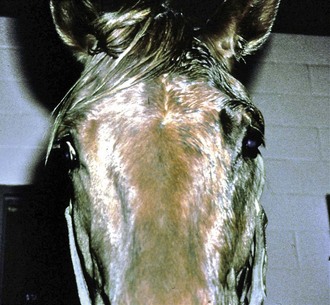
Green SL Cochrane SM Smith-Maxie L. Horners syndrome in horses is characterised by upper palpebral ptosis hyperthermia and unilateral sudoresis of the face and variable regions of the neck and trunk whereas enophthalmos third eyelid protrusion and miosis are less common signs. The prognosis depends on the inciting cause.
Horners syndrome also known as oculosympathetic paresis is a combination of symptoms that arises when a group of nerves known as the sympathetic trunk is damaged. Ipsilateral left facial sweating in horse with Horners syndrome following inadvertent perivascular jugular injection.
Horners syndrome in large animals The sympathetic nervous innervation of the head was surgically transected in the horse cow sheep and goat.
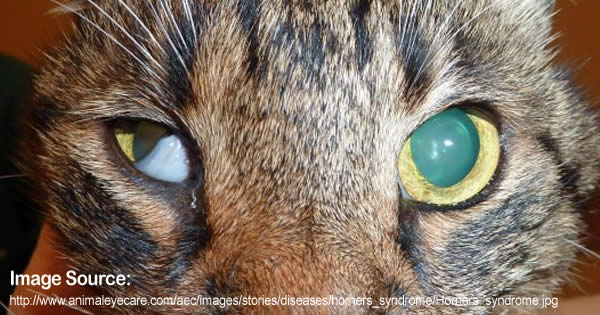
Grass sickness equine dysautonomia qv results in bilateral Horners syndrome. The most prominent symptoms of equine Horners syndrome were ptosis local. What is the prognosis Horners syndrome. The associated prominent ataxia however would leave little doubt of the anatomic diagnosis. Techniques in Eq Practice Vol 5 Issue 1 Mar 2006 pp. Horners syndrome in the horse. Hahn Miscellaneous Disorders of the Equine Nervous System. Sweating and ptosis were consistently observed by the attending clinician in over half of the affected horses. The condition is characterized by the sinking of ones eyeballs into the orbital cavity and anisocoria unequal size of pupils.
Palumbo M I P Moreira J J Olivo G et al 2011 Right-sided laryngeal hemiplegia and Horners syndrome in a horse. The condition is characterized by the sinking of ones eyeballs into the orbital cavity and anisocoria unequal size of pupils. Equine Vet Educ 23 9 448-452 VetMedResource. Ipsilateral left facial sweating in horse with Horners syndrome following inadvertent perivascular jugular injection. Horners syndrome also known as oculosympathetic paresis is a combination of symptoms that arises when a group of nerves known as the sympathetic trunk is damaged. The syndrome is named after the Swiss physician Johann Horner 1869 but the first report has also been attributed to Francois Pourfour du Petit in 1727. The findings in 6 experimental and 1 natural case of Horners Syndrome HS are presented.




























Post a Comment for "Horner's Syndrome In Horses"